Urban Wind Field - Introduction to URock
Introduction
Note
The tools in this tutorial are found in UMEP for Processing. The tool can be found from the menu (Plugins>Manage and Install Plugins).
In this tutorial you will make use the model URock to estimate wind fields in an urban setting using a semi-empirical wind model based on Röckle (1990).
URock can be used to calculate the 3D wind field of an urban area using information about the wind (at least speed and direction at a given height) and geographical data describing the area of interest (building and vegetation footprint and height). Two main stages are used: wind field initialization and wind field balance. For a detailed description of the model see, Bernard et al. (2023).
The model requires meteorological forcing data (wind speed and direction) and geometry information for buildings and trees.
Steps
Produce relevant input data needed to run the model using URock Prepare.
Run the model
Examine the model output using URock Analyzer
Initial Practical steps
UMEP for Processing is a Python plugin used in conjunction with QGIS. To install the software and the UMEP plugin (if not already installed), see the getting started section in the UMEP manual.
As UMEP for Processing is under constant development, some documentation may be missing and/or there may be instability. Please report any issues or suggestions to our repository.
Data for this exercise
The UMEP tutorial datasets can be downloaded from our here repository here.
Download, extract and add the raster layers (DSM, CDSM, DEM), the building polygon layer and the line profile layer into a new QGIS session. Coordinate system of the grids is Sweref99 TM (EPSG:3006).
To run URock, you need a building vector dataset including building height attributes and/or a vegetation vector layer including height and some additional optional info such as attenuation factor (see below). Here, you will make use of raster DSM, DEM and CDSM to generate information for URock.
URock Prepare
Open URock Prepare from the Pre-Processing section in UMEP for Processing found in the Processing Toolbox.
Use the settings shown below except for the output where you maybe need to specify a specific location on your computer where you have read and write access.
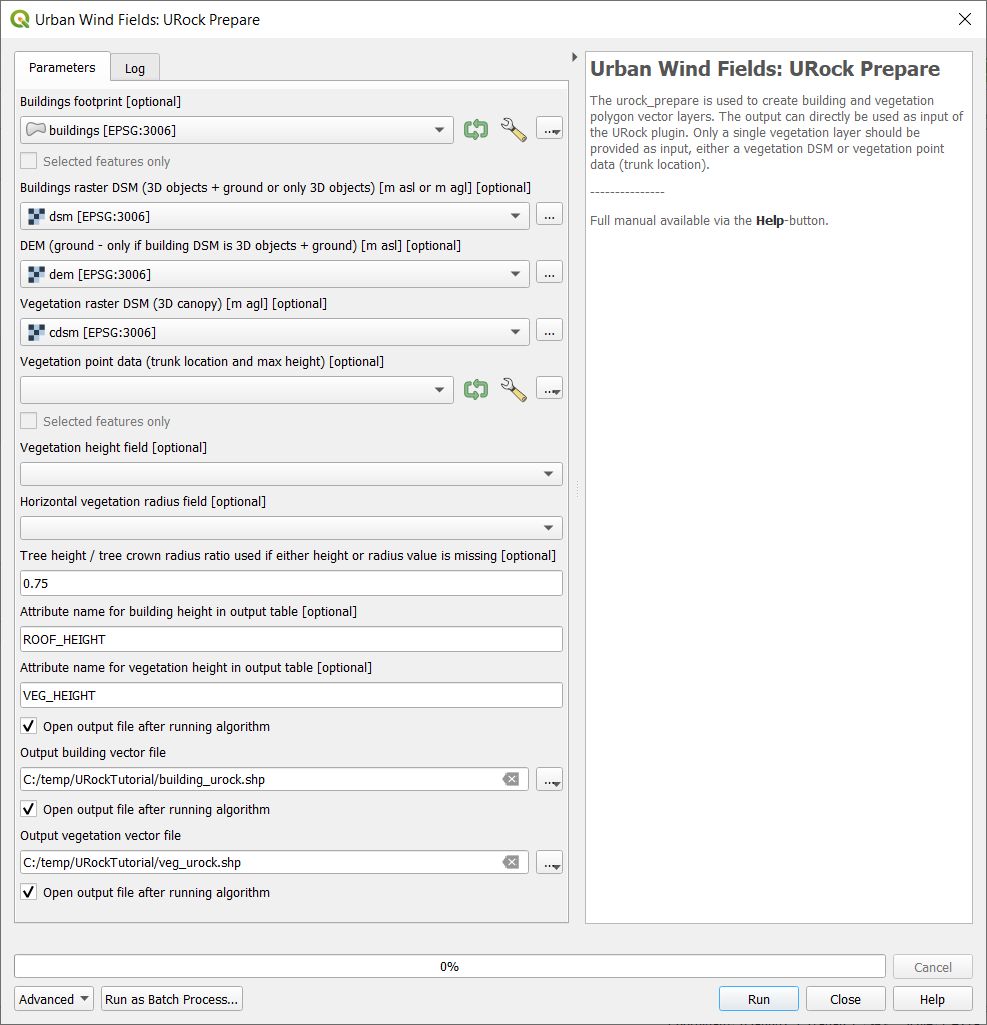
Fig. 114 Dialog for the settings in URock (part1)
If you have a dataset with points including tree location and attributes with heights and/or ratio information, this can also be used to generate vegetation data. Now click Run and two new files that are ready to use in URock will be created. The current version of URock does not include ground topography (hopefully available in upcoming versions). The DEM is used to derive building heights comparing the DSM and the DEM.
URock
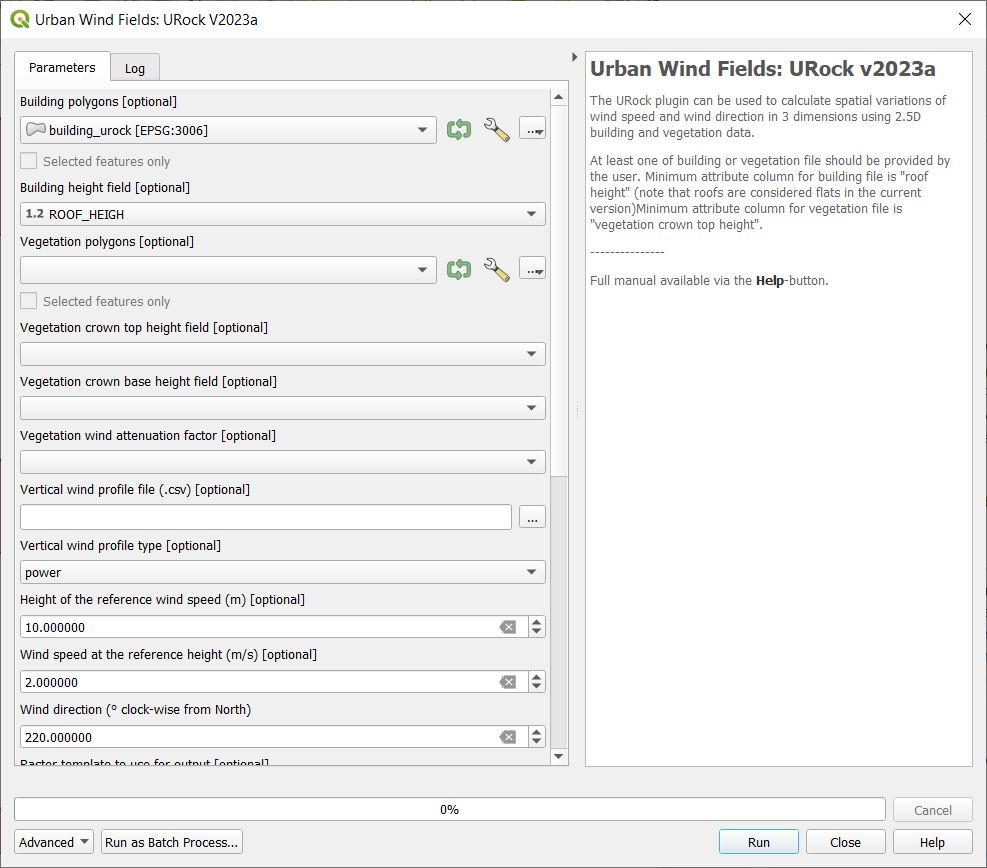
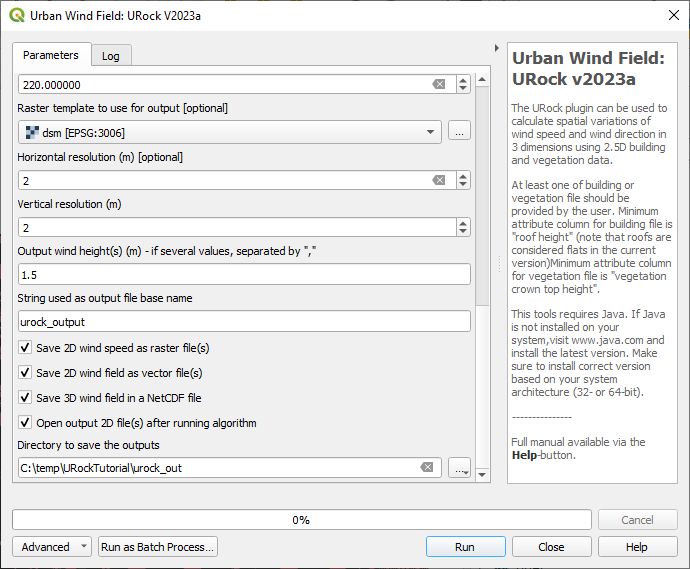
Open the URock interface (UMEP > Processing > Urban Wind Field: URock). Here you can make a lot of settings (divided into two figures). In your first run only buildings will be included and affecting the wind pattern:
When all the settings are made, click Run.
The computation will take some time depending on your computer standard. During the computation, you can follow the steps in the log-window in the URock-interface. A large part of the computation time is related to creation of all the different zones around buildings and vegetation. If you want an even more detailed picture of the process, open the Python Console in QGIS. However, this will somehow slow down the computational process. When the computation is finished, the tool will load the raster windspeed and the vector points at 1.5 meter above ground level.
URock Analyzer
With this tool you can examine your output more in detail by making vertical profile plots along lines and also calculating average wind profile within polygons. You will produce a line plot using the line vector layer (lineprofile.gpkg) included in the tutorial data.
Open URock Analyzer from UMEP > Post-Processor > Urban Wind Field: URock Analyzer and specify the settings as shown below:
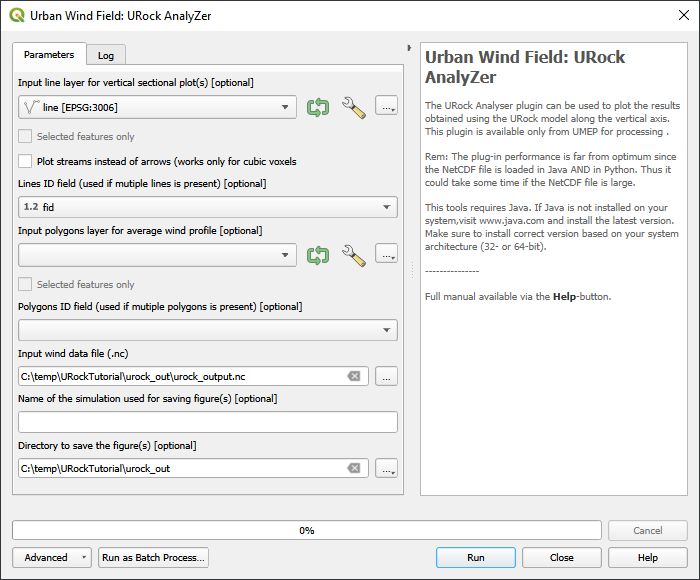
Fig. 117 Dialog for the settings in URock Analyzer
It is also possible to plot profiles from multiple lines if included in the vector file used for line profiles input.
Influence of vegetation on pedestrian wind
If you are interested, You can re-run URock and add the vegetation data. Then you just add your vegetation layer and specify VEG_HEIGHT as your vegetation crown top height field. Leave all other settings same as before except the output folder location. This will take longer time to compute (approximately 20 minutes on a regular laptop). When calculation is finished you can examine the influence that trees have on the wind within the model domain.
Tutorial finished.
References
Bernard, J., Lindberg, F., and Oswald, S.: URock 2023a: An open source GIS-based wind model for complex urban settings, EGUsphere [preprint], https://doi.org/10.5194/egusphere-2023-354, 2023.
Röckle, R.: Bestimmung der Strömungsverhältnisse im Bereich komplexer Bebauungsstrukturen, Ph.D. thesis, 1990.